
Improve your hearing health with Le Réseau Vos Oreilles!
For over 20 years, we have been helping thousands of people to hear better and improve their quality of life. Our professionals work with you to provide optimized audition and customized hearing comfort.
Click here to book your free hearing screening!
This offer is available at any time, regardless of your level of hearing loss. No medical referral is necessary.




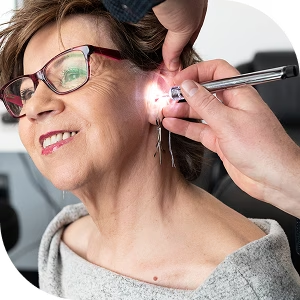
















We are at your side to take care of your hearing health.

Our services can be reimbursed
Our services and the price of our hearing aids may be reimbursed by some government agencies or insurance companies. We are here to inform you and explain the eligibility criteria and the steps to follow.
On-site audiology service
We work closely with audiologists in both the public and private sectors. For patients choosing a private service, audiologists work directly in our offices, facilitating the process and reducing waiting times.
A team at your service throughout Quebec
Whether you’re in the Outaouais, Greater Montreal or Mauricie areas, Le Réseau Vos Oreilles welcomes you to one of our 14 locations. Use our interactive map to easily find a hearing clinic or point of service near you!
Have you been exposed to noise in the workplace? Take advantage of your hearing health rights.
If you work in a noisy environment and have been exposed to loud noises for a long time, you may be eligible for the occupational deafness program from the CNESST (CSST) in Quebec or the WSIB in Ontario, even if you are retired.
Ringing or whistling in the ears (tinnitus), as well as difficulty following a conversation in a noisy restaurant, can be early signs of damage caused by prolonged exposure to noise. This program can help you obtain hearing aids free of charge.


Assistance in opening compensation files with the CNESST (CSST) in Quebec or the WSIB in Ontario
If you have worked in a noisy environment, you may be eligible for the CNESST (Quebec) or WSIB (Ontario) occupational deafness program, even if you are currently retired. We’ll help you with the administrative procedures related to occupational hearing loss.
OUR PRODUCTS
Enjoy high-performance hearing aids
Modern hearing aids offer much more than the simple correction of hearing loss. Thanks to advanced algorithms and artificial intelligence, they improve speech clarity in noisy environments and reduce unwanted sounds. Adapted to each situation, they act on your hearing health and positively transform the way you interact with the world.
Comfort and performance
We offer hearing aids tailored to your specific needs. Discreet, ergonomic and designed to fit the shape of your ears perfectly.
Simplicity and autonomy
Opt for freedom with our rechargeable hearing aids! No more batteries to change: enjoy a long-lasting, hassle-free power. Simply place your prostheses on their charger overnight, and you’re ready to go!
Connect to the world around you!
Our hearing aids feature the latest Bluetooth technology, enabling simple and secure pairing with your smartphone. Enjoy high-quality sound transmission for your phone calls, music, podcasts and even TV sound (adapter required) directly into your hearing aids, without having to wear bulky headphones.
Thanks to a dedicated application, you have access to precise, customizable settings: volume control, modification of listening programs, management of sound profiles according to your environment… Everything is designed to optimize your hearing comfort and meet the demands of the most complex situations.
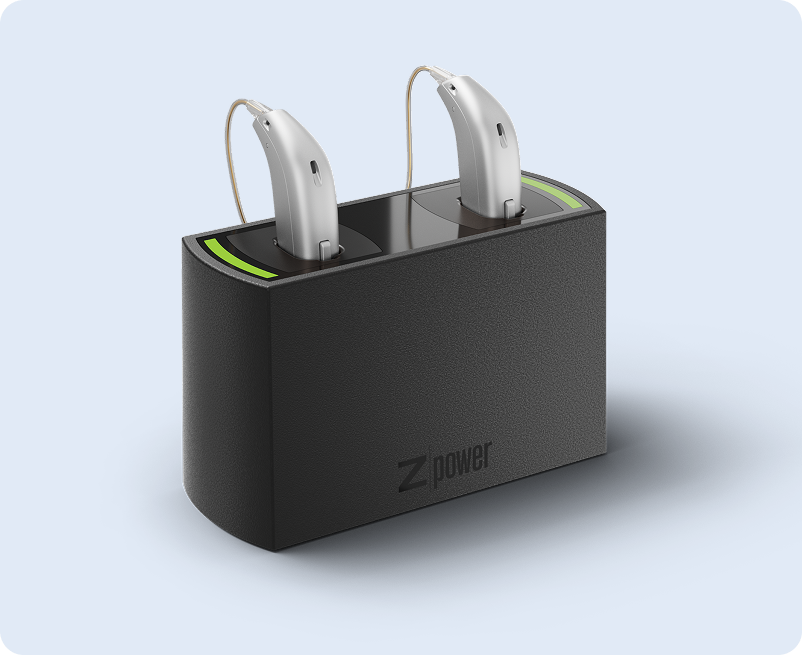


From personal experience to auditory innovation
Co-founder of Vos Oreilles, François Sasseville chose the field of audioprosthetics after experiencing hearing loss himself. This personal experience fuels his daily commitment to finding customized solutions designed to improve everyone’s quality of life. A great enthusiast of music and technology, François pays particular attention to providing clear, natural and pleasant sounds. Surrounded by an attentive and dedicated team, he does everything he can to ensure that every person who walks through the clinic’s doors feels listened to, understood and supported with kindness.
OUR SERVICES
We offer personalized hearing services
At Vos Oreilles, we know that every ear is unique. That’s why we take the time to listen to you.

Take care of your hearing today! Contact us for a free consultation and get back to hearing clearly.
Prevention is better than cure! According to Statistics Canada, 20% of the population has a hearing loss that could benefit from hearing correction. Don’t wait, consult us at the first signs of hearing difficulties, whatever your age. Hearing screening is offered free of charge at all times. Take care of your hearing right away. You’ll be delighted with our personalized service and state-of-the-art equipment.
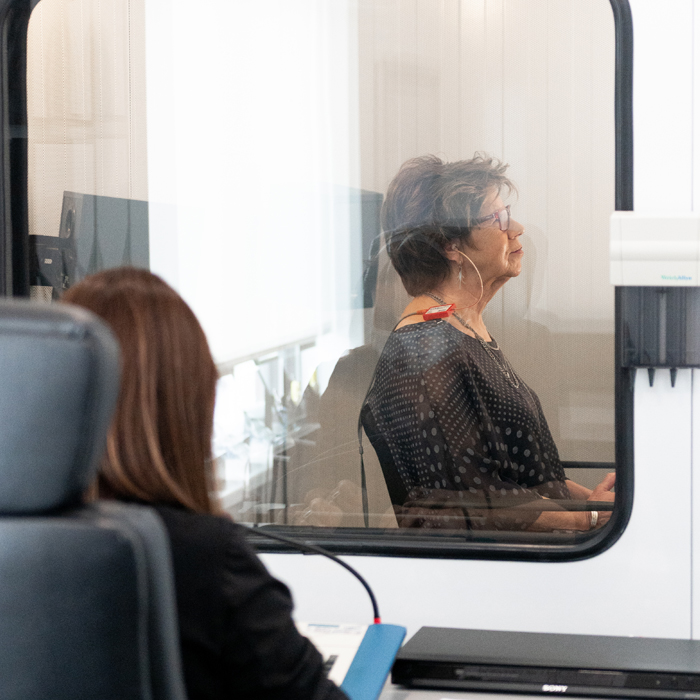

To make sure you receive complete care that truly fits your needs, we work closely with a trusted network of healthcare professionals, including ENT specialists, audiologists, and family doctors. If necessary, we’ll be happy to connect you with these qualified, dedicated experts, so you benefit from personalized, high-quality support at every step of your hearing journey.
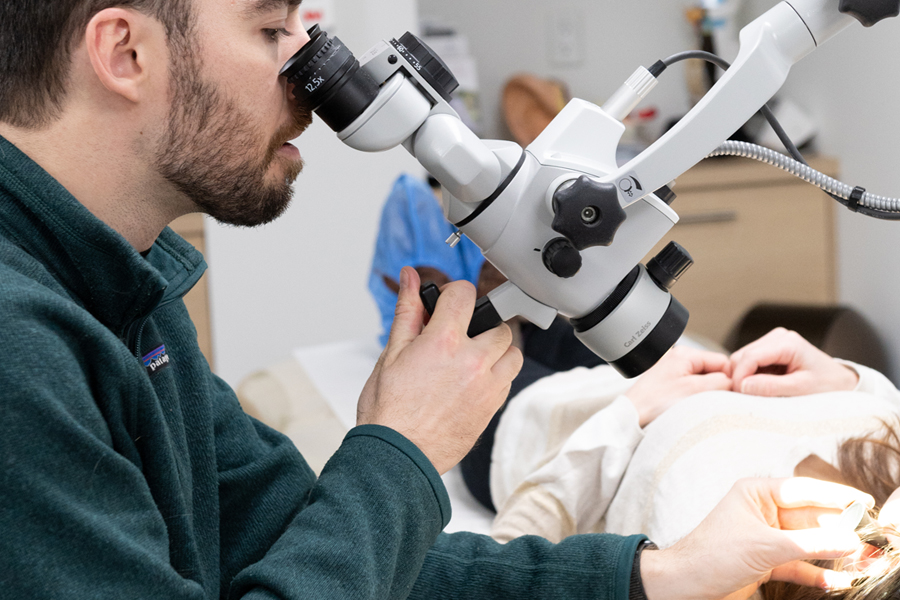

Do you hear a buzzing, whistling or crackling sound?
Tinnitus can be disturbing, but there are treatments to help. Did you know that wearing hearing aids is the number one recommended treatment for tinnitus? Thanks to advanced technologies and personalized monitoring, our audioprosthetists will help you find the solution that will relieve your hearing discomfort.
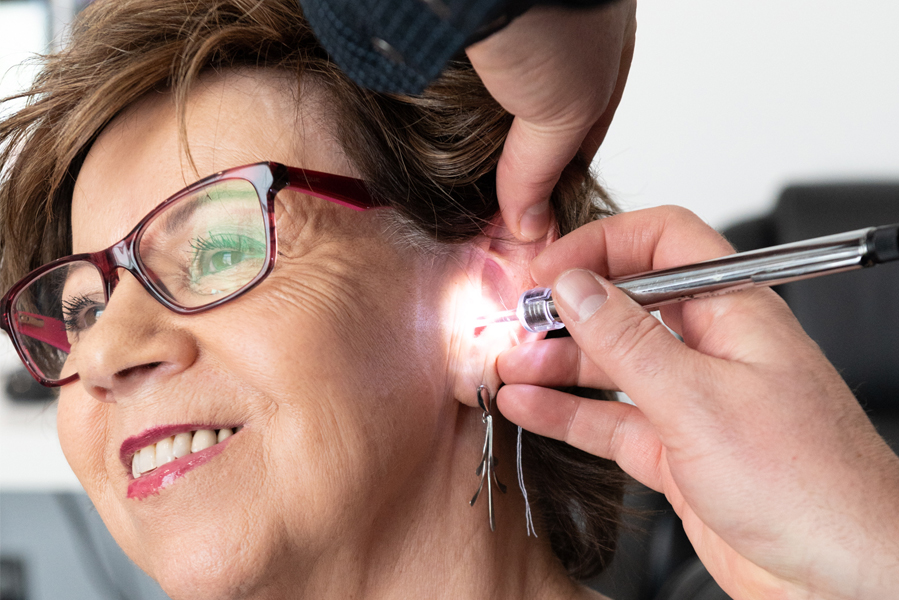
Whatever your needs, we can refer you to audiologists in the public system or in private practice. Contact us today to get a comprehensive hearing assessment.
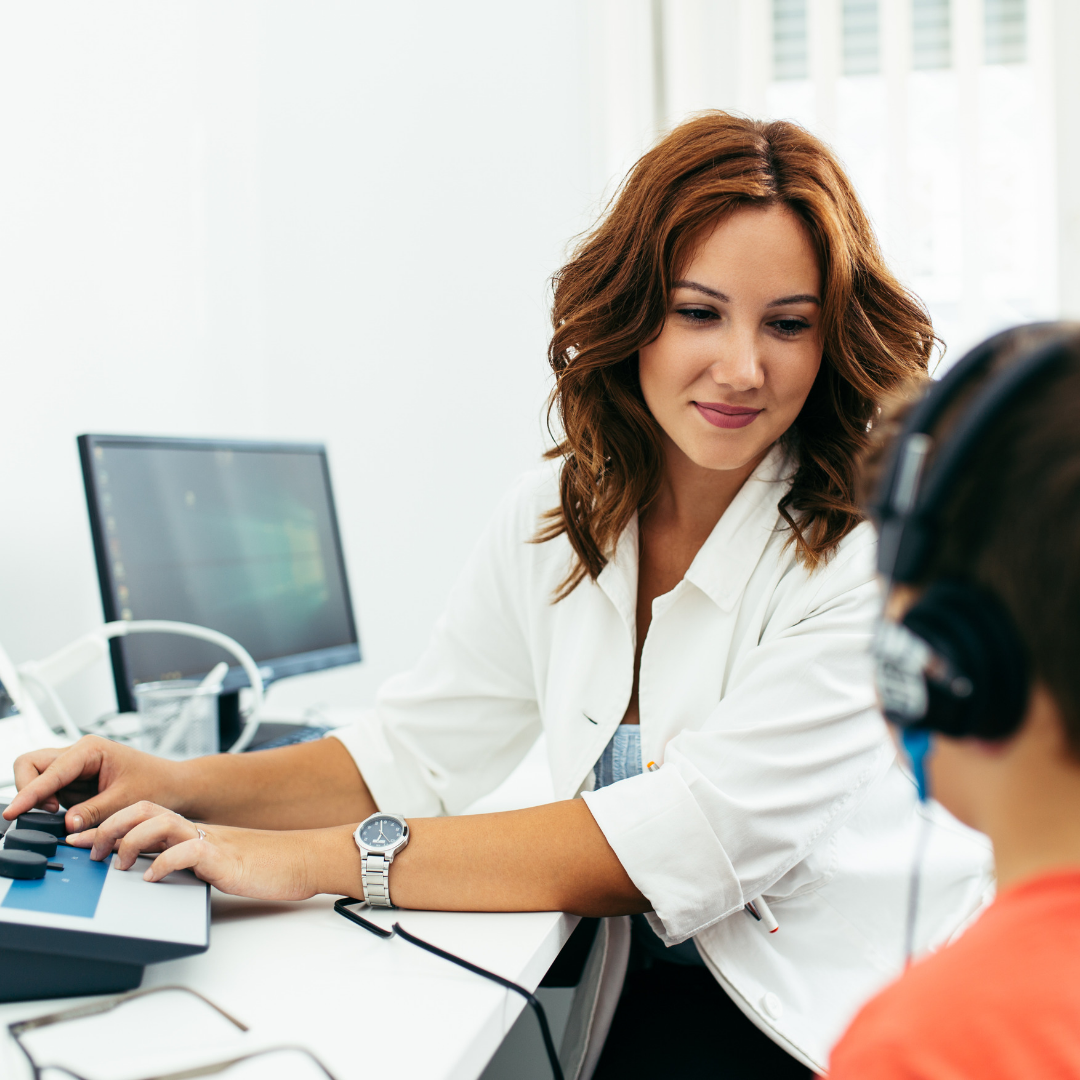

Choosing your hearing aids is much more than a simple decision: it’s the key to regaining real comfort in everyday life, and enjoying your sound environment to the full.
Our hearing care professionals will help you make this important choice, taking into account your needs, expectations and budget. Thanks to their expertise, they can guide you towards the most suitable models and technologies, from a wide range of discreet, high-performance solutions.
Our commitment: to offer you maximum hearing comfort and a natural, long-lasting, uncompromising listening experience.
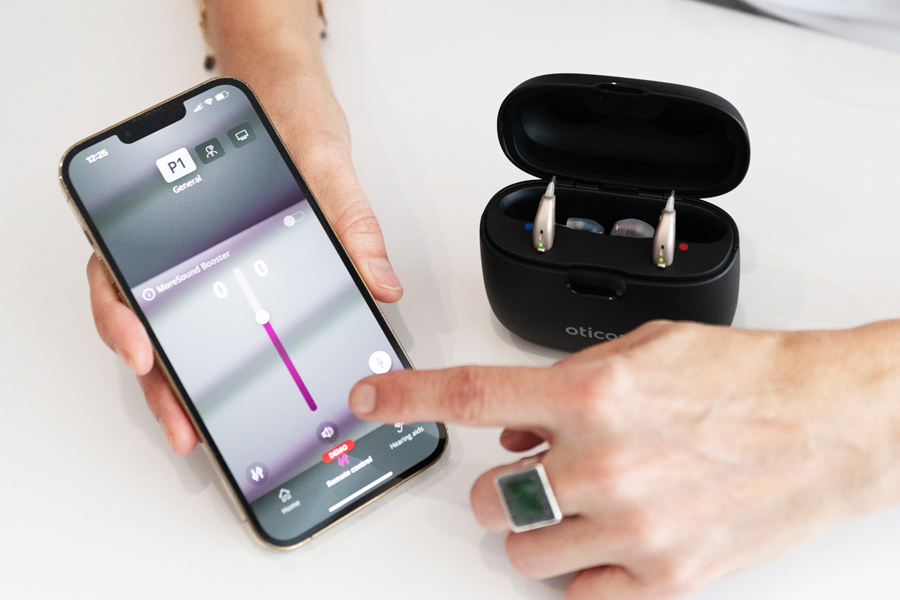

Adjusting your hearing aids is essential to providing you with natural hearing adapted to your needs. We use state-of-the-art tools to personalize each setting according to your hearing and environment. This process offers you optimal sound reproduction and everyday comfort.

We know how essential your hearing aid is to your quality of life. If you encounter a problem with your prostheses, our professionals are available to repair all types of devices, regardless of brand.
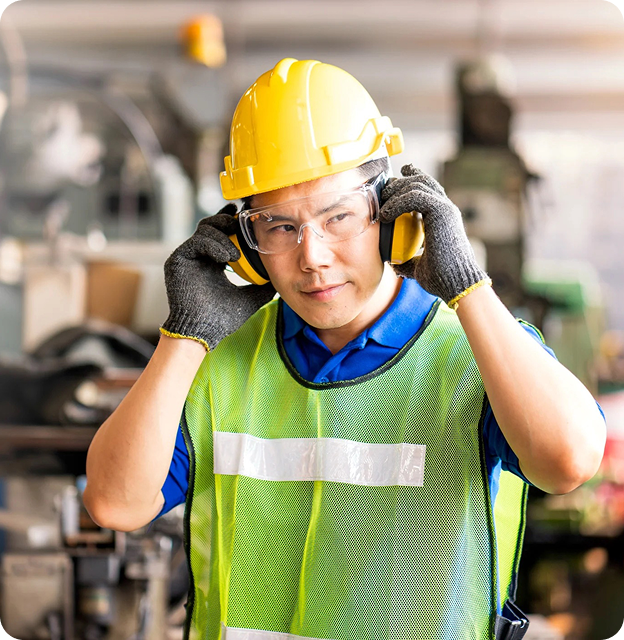

Make the most of our support service to open a file with paying agencies such as CNESST, WSIB, RAMQ and many others. Whether you qualify for a work-related hearing loss compensation or a government-funded hearing aid, we’ll guide you through every step of the process.

Have you been exposed to noise in the workplace? Take advantage of your hearing health rights.
If you work in a noisy environment and have been exposed to loud noises for a long time, you may be eligible for the occupational deafness program offered by the CNESST (CSST) in Quebec or the WSIB in Ontario, even if you are retired. Ringing or whistling in the ears (tinnitus), as well as difficulty following a conversation in a noisy restaurant, can be early signs of damage caused by prolonged exposure to noise. This program could help you obtain hearing aids free of charge.
WHAT'S THE NEXT STEP?
Hearing loss?
Here's the solution in 3 easy steps!
Hearing health is within everyone’s reach, and we’re committed to supporting you every step of the way.
1. Consult our qualified audioprosthetists dedicated to your health
Our audioprosthetists, members of the Ordre des audioprothésistes du Québec, are committed to constantly improving their knowledge in order to offer you services on the cutting edge of advancement in hearing health.
To ensure comprehensive, personalized care, we work closely with other healthcare professionals, such as doctors, ear, nose and throat (ENT) specialists and audiologists. Together, we do everything possible to guarantee you the hearing solutions best suited to your needs.
2. Hearing screening
Take advantage of our free hearing screening service, available all year round. In just a few minutes, we can quickly and easily assess your hearing abilities.
This painless test is performed in a soundproof booth, using high-precision equipment for immediate, reliable results. Take care of your hearing today. All it takes is an appointment!
3. Receive hearing aids adapted to your needs
Treat yourself to the best of hearing technology!
At Réseau Vos Oreilles, we offer the most advanced, high-performance brands and models of hearing aids on the market. Thanks to our expertise, we can guide you towards the ideal solution, perfectly tailored to your needs… and your budget! Sophisticated, discreet devices designed to transform your daily life.
WHAT'S THE NEXT STEP?
Hearing loss?
Here's the solution in 3 easy steps!
Hearing health is within everyone’s reach, and we’re committed to supporting you every step of the way.
1. Consult our qualified audioprosthetists dedicated to your health
Our audioprosthetists, members of the Ordre des audioprothésistes du Québec, are committed to constantly improving their knowledge in order to offer you services on the cutting edge of advancement in hearing health.
To ensure comprehensive, personalized care, we work closely with other healthcare professionals, such as doctors, ear, nose and throat (ENT) specialists and audiologists. Together, we do everything possible to guarantee you the hearing solutions best suited to your needs.
2. Hearing screening
Take advantage of our free hearing screening service, available all year round. In just a few minutes, we can quickly and easily assess your hearing abilities.
This painless test is performed in a soundproof booth, using high-precision equipment for immediate, reliable results. Take care of your hearing today. All it takes is an appointment!
3. Receive hearing aids adapted to your needs
Treat yourself to the best of hearing technology!
At Réseau Vos Oreilles, we offer the most advanced, high-performance brands and models of hearing aids on the market. Thanks to our expertise, we can guide you towards the ideal solution, perfectly tailored to your needs… and your budget! Sophisticated, discreet devices designed to transform your daily life.
Schedule your free initial consultation!
You have questions or would simply like to talk to a hearing health professional about your hearing difficulties? Book an appointment now. This no-cost offer is available at any time and requires no medical referral.
Test your hearing online
Use one of our two tools to detect the early signs of hearing loss.
Find a hearing clinic or point of service near you
Consult our directory to find a clinic or point of service near you!